
I: Introduction
One thing we can all agree on is that the world today is at its most screwed up in a very, very long time. What we don’t necessarily agree on is who in particular is at fault, who in particular has to be removed from power, and what is the best way to remedy these problems.
At the heart of these problems is one man, whom I affectionately call Orange-face (I call him by this moniker in case any liberals in the comments mistake me for an apologist of his). The Trump phenomenon is a classic case of controlled opposition: either you worship him in a cult of personality, or you abominate him to the point of Trump Derangement Syndrome.
What you’re not supposed to do is to regard him as yet another example of the capitalist class using a demagogue to further their interests. They want us to focus on individual personalities as a distraction from the very group of people who are really behind all of the injustices of the world, people of whom Trump is just one example.
The ruling class is thrilled to have us either demonize Trump as the supposedly sole cause of our problems, or to worship him as the sole solution to these problems. The bourgeoisie would be terrified if we fingered them as the true cause of our problems, for then we might be motivated to overthrow them, not just vote in a “lesser evil” and gain satisfaction from how the new president is, at least, ‘not Trump’ (though the new policies will remain largely the same).
Apart from those in the MAGA crowd who have finally seen the light and realized that Trump isn’t doing anything to improve the lives of Americans, there are still a number of red-cap-wearing morons out there who turn a blind eye from such things as the Gaza genocide (which he’s enabling no less than the Biden administration did), the regime-change operations and other forms of imperialism (so much for the “peace-loving president”), and the Epstein scandal, not to mention the “corporatism” of his political love affair with all those tech-bros.
What the MAGA crowd and the TDS liberals have in common is their misguided belief that Trump, for good or ill, represents a huge shift in American, and therefore global, politics. The MAGA crowd continue to delude themselves that Trump is ‘draining the swamp’ and taking on the ‘deep state.’ Liberals wail, gnash their teeth, and rend their garments thinking that his second administration is an abominable deviation from how America ‘ought to be.’
To be sure, things have gotten recognizably worse since 2025, but the worsening of the world has had far less to do with his personality than it has had to do with the general worsening of things ever since the dawn of neoliberalism and the dissolution of the USSR. Let’s now go into all of the conditions that have led to Trump, and therefore learn how he is no aberration from the system, but rather, he’s its culmination.

II: Fascism
It would be a naïve mistake to think that people like Hitler or Trump are these unique monstrosities who suddenly popped out of nowhere. They didn’t pass through a membrane from another dimension. Their rises to power were a result of particular material conditions to serve the needs of the ruling class at those particular times.
Fascism in general is used by the capitalist class as a response to crises in capitalism, when the system is breaking down, and there’s a danger of the working class rising up in revolution. There were Mussolini’s blackshirts physically assaulting Italian leftists in the 1920s. There were the Nazis putting German leftists in the first of their concentration camps. And now, there’s the designation of Antifa as a ‘domestic terrorist organization’ (when it really isn’t any kind of formal organization, but just an umbrella term to describe antifascism in general…and how exactly is that a bad thing?), and there’s the intention to use ICE to target leftists.
What is more important to understand, though, for the purposes of this argument, is that fascism and ideas associated with it are far from anything new in the US. What I’m saying here is hardly eye-opening to any leftist, of course, but those of my readers in the political centre and to the right may need a bit of a history lesson.
Far from being ‘a shining example of freedom and democracy for the world,’ the US was built on black slavery, the genocide of the Native Americans, and it’s therefore a shining example of white supremacist settler-colonialism. Racism against blacks was only the tip of the iceberg.
Hitler’s fantasies of achieving lebensraum for the ‘Aryan race’–the conquering and settling of Eastern Europe and the enslaving or killing of Slavs–was inspired by American Manifest Destiny and the Monroe Doctrine. Slavs were understood to be the Nazis’ equivalent to the Native Americans, an ‘inferior’ race meant to be subjugated. Naziism didn’t inspire people like Trump: people like Trump inspired the Nazis.
After WWII, the American government, NATO, and West Germany gave jobs to ex-Nazis to help fight the Cold War–Operation Paperclip. The Ukrainian underground (which included the Nazi-sympathizing OUN) was also given help by the West to fight communism–Operation Aerodynamic. Operation Gladio was set up in Europe in the 1970s, using fascists there to fight communism, too.
In 2014, the US and NATO aided in a coup d’état to remove Ukraine’s democratically-elected president, Viktor Yanukovych, to set up a US-friendly government that includes Nazi sympathizers. The purpose of this was to stop Yanukovych’s pro-Russia, anti-IMF stance, so the US and NATO would have more control over Ukraine, as was demonstrated in Victoria “fuck the EU” Nuland’s telephone call with Geoffrey Pyatt, then-ambassador to Ukraine. Provoking Russia into war with Ukraine, then blaming Russia for the war, was all part of the plan.
Trump may pay lip service to wanting to stop the Russian/Ukrainian war (probably more to win votes in the 2024 election than out of a sincere desire to have peace), but his ‘peacemaking’ stance doesn’t explain his willingness to sell Javelins to Ukraine back in 2017. He couldn’t stop that war even if he wanted to, anyway: too many billions have been invested in it from the Biden administration.
In short, the support of fascism is as American as apple pie–it didn’t start with Trump.

III: Greenland, Venezuela, and Cuba
Trump’s recent threats to take Greenland are seen as a highly eccentric move by him, to put it mildly. But as Dennis Riches demonstrated in a blog post, the American desire to take Greenland (typically by purchase) is nothing new. Attempts to purchase Greenland go back to Seward in 1867, when Alaska was purchased. Other attempts before Trump to acquire it were in 1910, 1945-1946, and 1955. Trump’s more aggressive attempts to acquire Greenland are thus the culmination of them, not a deviation from a previous American contentment with leaving the island alone.
As is the motive for so much of US imperialism, that of obtaining Greenland is a combination of economic and geo-strategic ones: the island possesses potential reserves of hydrocarbons and rare minerals crucial for high-tech industries; economic valuations are estimated to range from $200 million to as high as $1.7 trillion; and Greenland’s location is crucial for military and ballistic missile trajectories between the US and such major powers as Russia and China (hence, Trump’s rationalizations about American ‘national security’ vis-à-vis Greenland).
As with the kidnapping of Nicolás Maduro and the threats to overthrow the Venezuelan government, the threats on Greenland reflect an arrogant American attitude that the US somehow ‘owns’ both American continents and every piece of land that’s a part of them. It’s nothing new: the US regards South America as its ‘backyard’; Manifest Destiny would have all of North America (including Greenland) to be part of the US eventually; and the Monroe Doctrine would refuse any foreign intervention in the Western Hemisphere, certainly not out of any sensitivity to the sovereignty of the countries within that area, but because–let’s face it–the US government imagines that it owns all of this land (as an extension of the Monroe Doctrine, the Roosevelt Corollary makes my interpretation more explicit).
The motive to control Venezuela is obvious, and even openly admitted by Trump: to steal their oil, of which Venezuela has the largest reserves in the world. Only an idiot thinks confronting Venezuela is about drugs. Many attempts have been made over the years to wrest power away from those protecting the Bolivarian Revolution. A coup tried to unseat Hugo Chavez during the George W Bush administration. Starvation sanctions have been imposed on Venezuela for years. Again, Trump’s attacks on the country are the culmination of years, decades, of toxic US foreign policy. It isn’t just about Trump being an asshole.
As for Cuba, Trump’s threats are only the latest in decades of attacks on the island, from the failed Bay of Pigs invasion, to the economic embargo that’s lasted over six decades, to the hundreds of attempts on Fidel Castro’s life. Trump is the culmination of it all.

IV: Epstein
Only a fool thinks Trump is anything other than guilty as sin when it comes to the Epstein files. Was it ever a secret that he’s an old lecher? The man openly lusts after his own daughter! We’re supposed to believe that he, with his money and connections with the billionaire class, did not rape underage girls on Epstein island?
The MAGA crowd, still delusional that ‘God sent Trump to take on the deep state,’ will do mental gymnastics and believe him that the Epstein scandal is a conspiracy to bring him down. They’ll also try to deflect criticism from him by pointing out how men like Bill Clinton are also guilty of involvement in the goings-on with those girls, goings-on that sound like something out of a Marquis de Sade novel, or Salò, or that scene in the mansion in Eyes Wide Shut. I’m perfectly content to see Clinton shamed and punished, too, for I’m not partisan.
The point is that, apart from the disgusting sexual abuse these men are guilty of, the Epstein files expose something that should be obvious to everyone: people with obscene amounts of wealth feel free to commit the most obscene acts of violence, sexual or otherwise, against the poor and vulnerable, because they can simply buy their way out of being accountable for it.
We shouldn’t be the slightest bit surprised that Jeffrey Epstein was a Mossad agent (that some are claiming he was a Russian agent is the most desperate Hasbara!). It makes so much perfect sense as to be a no-brainer that there would be a link between a Mossad agent and members of the ruling class raping underage girls, on the one hand, and on the other, the enabling of the Gaza genocide. These people have nothing but contempt for human life.
Another thing to keep in mind: the Epstein people got caught. How many other people among the super-rich have committed the same kinds of crimes elsewhere, and at other times in history, and gotten completely away with it? Very few of the current gang of criminals have been punished: Ghislaine Maxwell is incarcerated, and is Epstein even dead…murdered, or the unlikely official explanation? He’d have the money and connections to make himself disappear, even if those photos that surfaced are faked, as some claim they are–a little plastic surgery, and he could live anonymously somewhere in Israel, with bodyguards to protect him.
It seems unlikely that the rest of the guilty will ever be punished, beyond a public shaming. In any case, we’re dealing with the crimes of the rich that hardly started with Trump, and–outside of a socialist revolution–will likely continue to be perpetrated long after he’s gone.

V: Israel
It’s fitting to follow up the above Epstein section with this one on Israel since, as I mentioned above, he was an Israeli agent. It’s also fitting because the Zionist regime is also guilty of committing some of the most heinous crimes against humanity, against women and children in particular, and crimes that, in all likelihood, will never be punished outside of a revolutionary overthrow of the entire global system. These crimes have in common with those of Epstein’s criminals a contemptuous disregard for the rights of the vulnerable and the poor.
A lot of people say that Israel has used the Epstein files to blackmail Western politicians into doing the bidding of the Zionists. Such coercion hardly seems necessary, given how thoroughly willing most in the upper echelons of Western politics are to support Israel. Epstein and Maxwell, as well as Trump, Clinton, Prince Andrew, and others have already been outed: where’s the power of blackmail? Epstein and Maxwell were arrested. Nobody else to date is being punished.
The notion of Israeli blackmail is surely rooted in the antisemitic canard that Israel rules the world, which in turn is rooted in the idea that the Jews rule the world–Nazi nonsense. The correct way to understand Israel’s relationship with the world, as I’ve discussed elsewhere, is that Israel is a vital ally to the Western empire. That tiny sliver of land is in a crucial area of the world geo-strategically, where there’s so much oil and thus such a great need to control the area. The Western empire needs an ally there to kick ass among unruly neighbours who don’t want that Western control and exploitation going on.
Because capitalism, as we know through Lenin, is intimately connected with imperialism (i.e., the export of capital into other countries and stealing their resources to get rich off of them), it’s easy to see how the super-rich would have always enthusiastically supported Israel as a protector of Western interests. Just as the concentration of wealth among the 1% is nothing new or started under Trump, neither is the abuse of the vulnerable, on Epstein island or in occupied Palestine. Trump’s abuses are the mere culmination of it all.
Israel’s founding in 1948 was land theft, plain and simple. The Zionists never had, and still don’t have, any right to that land. Israel as a country should not exist; Palestine belongs to the Palestinians. It’s perfectly acceptable, on the other hand, to have Jewish communities in Palestine, even large ones, enjoying full equal civil rights there with the Muslims and Christians…but not superior civil rights. Such Jews would be Palestinian Jews, not Israeli ones–therein lies all the difference. As for the excess of Jewish settlers, however, they have the right to pack up their bags and leave, as Norman Finkelstein once said.
The Soviet Union, regrettably, in a momentary lapse of reason and rationalized as realpolitik, aided in the establishment of Israel, hoping to gain geopolitical leverage in the region and–with a ‘socialist’ Jewish state–gain a crucial ally. The Zionists’ choice to side with the US and capitalist West took away the USSR’s illusions about the new country, and the Soviets quickly repented and maintained all solidarity with the Arabs from then on.
US support for Israel ever since, from both the GOP and the DNC, has of course been unwavering. Even “progressives” like Bernie Sanders and AOC, for all of their paid lip service to opposing Netanyahu, support Israel’s “right to exist” and insist on condemning Hamas, whose necessary armed resistance against Israel has been shown to be more than justified over the past few years of carnage in Gaza.
Biden and Harris willingly green-lit the genocide in Gaza, right from October 2023 until the end of their administration, and if Harris wins in 2028, there’s no reason to believe she’ll change her stance. All talk of her having ‘worked tirelessly’ to end the killing of Palestinians was and is just that…all talk. Trump’s moving of the American embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem on May 14th, 2018 (the 70th anniversary of the nakba), and his current wish to turn the mass graveyard of Gaza into a set of resorts for wealthy vacationers, as outrageous as these are, are merely the culmination of a decades-long project of ethnic cleansing.
No blackmail is needed to make Trump, or any of the other plutocrats, support Israel, for such support is already in their class interests. They want to maintain a global order that ensures more for themselves and less for everyone else. Support of Israeli settler-colonialism–just like that of the US, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, etc., as against the rights of the indigenous peoples of all of these ‘countries’–is integral to maintaining such a world order. Socialism is anathema to such a system, and that’s why billionaire Israeli agent Epstein was the very antithesis of socialism. The only way Israel needs to blackmail the West is through its most probable nuclear weapons program and the Samson Option, that is, if any attempt is made to overthrow the Israeli regime.

VI: ICE
ICE, having received training from the IDF (and having a similar contempt for human life), can be seen as a manifestation of the imperial boomerang. Now, I don’t mean “boomerang” in a strictly geographic sense, since fascist terrorizing of people of colour in the United States is nothing new. Hear the words of black Americans when they describe their victimization from police brutality to know what I mean. The violence has, however, boomeranged on white people, and while we shouldn’t use this violence to prioritize whitey and minimize the horror that should be felt at state violence against POC, we can use this new violence to point out the extremes to which the state is going now.
When an otherwise white supremacist culture is actually starting to inflict violence on people of their own skin colour, people they normally take it easy on, things have come to a pretty pass, to put it mildly. We’re horrified to contemplate the Nazi murder of Jews, the Roma, Slavs, etc., but not quite so much when King Leopold II of Belgium was responsible for the butchering of one to fifteen million Congolese. Similarly, the condemnation of the 1985 MOVE bombing isn’t quite as vehement as it should be.
My point is that we shouldn’t regard the ICE atrocities as either anything new or anything occasional in history. That many are shocked at what ICE is doing now is merely an indicator of how little they seem to be aware of such violence against non-whites for many decades…centuries. That ICE is attacking whites and American citizens now is an indication of the boomerang I’m talking about.
And while the ICE attacks have gotten particularly vicious under Trump, we shouldn’t regard the problem as just a ‘Trump thing.’ Anyone who has been following the history of ICE knows that the Democratic Party has done much over the past two decades to strengthen the law enforcement agency.
ICE was created in 2002, under the Bush administration, as part of the Homeland Security Act in response to the 9/11 attacks. There was already severe criticism for ICE’s aggressive, militarized attacks, including high-profile workplace raids, the separation of families, and civil rights violations.
ICE was awful under the administration of Obama, the “Deporter-in-Chief,” too. They deported a record 2.4 million undocumented immigrants, 40% of those deported in 2015 having no criminal conviction, and a majority of those convicted guilty of only minor charges. See here for an investigation of complaints of abuse and harsh treatment in the detentions and deportations during Obama’s first term, aired in 2011, and how it all continued in his second term.
The Democrats have helped in the increase of funds to ICE. The inhumane conditions of ICE detention centres continued under the Biden administration. The beefing-up of the agency during the second Trump administration should not be seen as an aberration from a ‘normal’ form of deportation, but as the culmination of targeting POC, finally rebounding and hitting whites, too.

VIII: Iran
The current push for regime change in Iran (while there are some Iranians with legitimate grievances against their government, the bulk of the recent protesting and violence in the country has been sparked by US and Israeli influence, not least of all by the sanctions imposed there causing economic misery) is, of course, not an aberration from usual American foreign policy. The Trump administration is just carrying on a continuation of a decades-long policy.
It can be traced back to when Mohammad Mosaddegh tried to nationalize Iranian oil in the early 1950s, wishing to use the revenue to improve the lives of his people rather than allow the West to exploit it and profit off of it. Of course, such ‘socialism’ could not be tolerated, and the MI6 and CIA helped bring about a coup d’état in 1953 to get rid of Mossadegh and install the Shah, a Western puppet who’d ensure that the exploitation continued.
The Shah, Mohammed Reza Pahlavi, would no longer be tolerated by the Iranian people by the late 1970s, and he was overthrown in 1979 to establish the Islamic Republic of Iran, then led by the Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini. During the Iran/Iraq War in the 1980s, the US gave aid to Saddam Hussein, even with him using chemical weapons on Iranian forces, fearing that an Iranian victory would threaten regional stability and oil supplies (Of course, there was some US aid to Iran, too–i.e., the Iran Contra Affair; but it was mostly about aiding Iraq.).
Israel has always felt threatened by a strong Iran, so naturally the US will snap to attention and aid the Zionists. A reflection of that US/Israeli solidarity, among so many of them, can be seen from back when Dubya spoke of Iran, Iraq, and North Korea as an “Axis of Evil,” propagandistically exploiting quasi-Nazi language as a projection of American fascism on the three “rogue” countries just after 9/11.
The sanctions imposed on Iran, ever since 1979, have devastated the country, causing banks and firms to withdraw humanitarian trade; this has left Iranians with rare and severe diseases unable to obtain the medicine and treatments they need. The desperation felt there, combined with how the Mossad has been stirring things up, more than explains the explosion of violence in Iran. The Western hypocrites couldn’t care less about human rights issues: they just want a US/Israel-friendly regime installed there. It should come as no surprise that the former Shah’s son is to be Iran’s next head of state.
Overthrowing the Islamic Republic of Iran won’t exactly thwart the BRI, but it will certainly disrupt it, as Iran is a key component of it, and the West would like to hinder it. In any case, between attempts to overthrow the governments of Iran and Cuba, and to take Greenland, the American empire is clearly overextending itself, and history has taught that empires that do so are not long for this world.
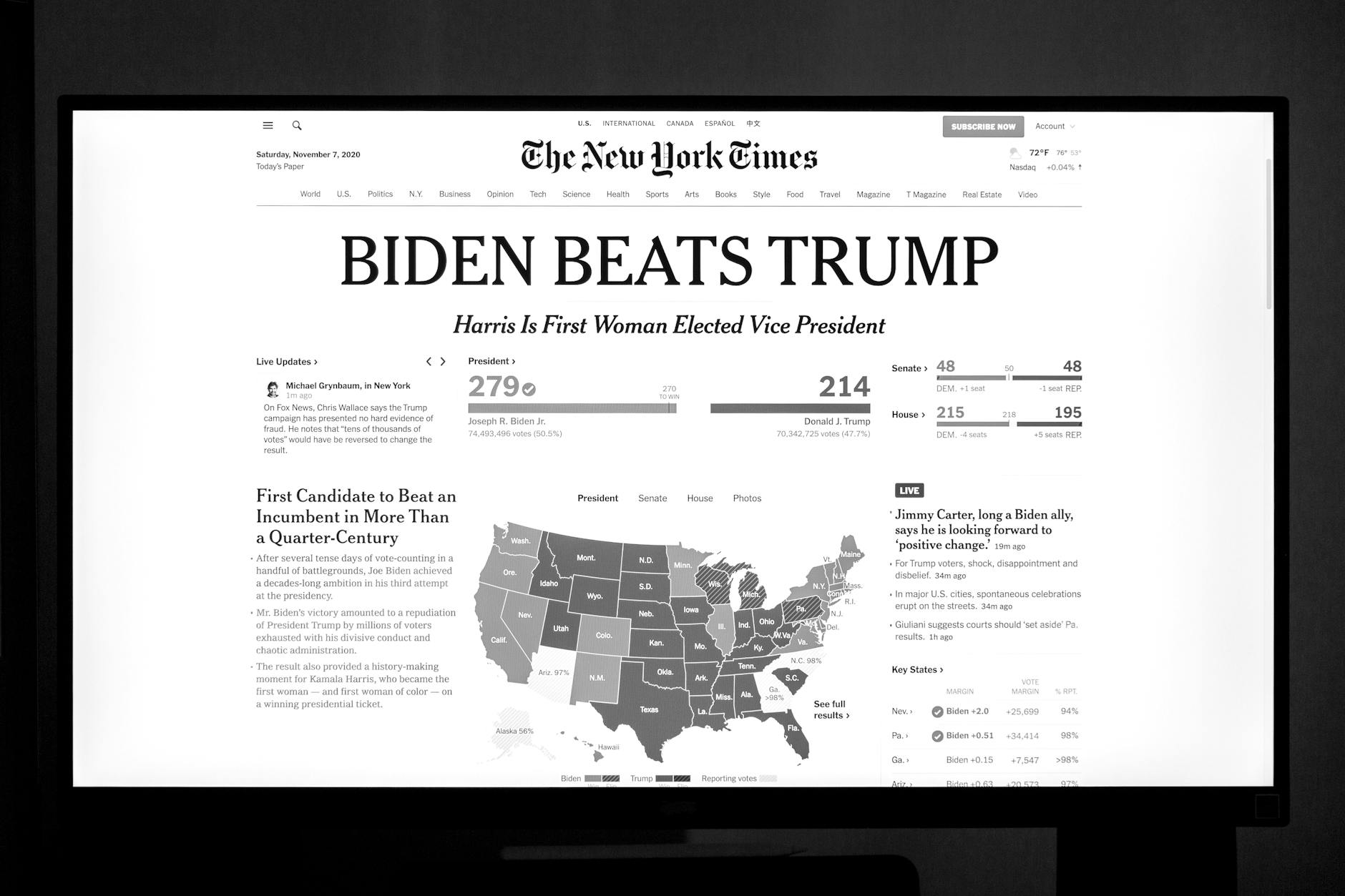
VIII: Democrats Helping to Pave the Way
I’ve already pointed out how the Democrats are at least partially responsible for such problems as the support of Ukrainian Nazis, links with Epstein (i.e,, the Clintons), support for Israel and the Gaza genocide, the increase of funds to ICE, and the sanctions on Iran. There’s much more, as I’ll soon go into, and have gone into in previous blog posts.
The point I’m trying to make here is that it is beyond naïve for liberals to think that a mere voting in of Democrats will solve the Trump problem. In fact, it’s outright political dishonesty. Liberals being “at brunch” if Hillary or Harris had been elected means they would have turned a blind eye to Epstein, Gaza, ICE, and Iran. They certainly would have been cheering on Ukrainians fighting to the last man against their bogeyman, Putin, meaning they’d be content to see all Ukrainians die in the process (what “To the last Ukrainian!” really means), while smugly blaming Russia for a proxy war the US and NATO provoked.
To get rid of Trumpism, one has to get rid of the conditions that gave rise to Trump, and the Democratic Party’s concessions to the rise of the right have been key to creating those conditions. Liberal claims that bipartisanship makes for “better legislation” (yes, I know a shit-lib who actually said that online, and I’d say it’s a safe assumption that there are many shit-libs out there who’d say, and have said, the same thing) is their outright confession that they are a crucial part of the problem.
If one goes into the history of it, it isn’t difficult to see how right-wing libertarianism leads to fascism. First, they cut taxes on the rich and deregulate the economy, so businesses can make higher profits. This sort of thing happened under Reagan and Thatcher. It also turned millionaires to billionaires, who could then buy both political parties via Super PACs and make them steer politics in even more pro-business directions. This is all why notions of the “free market” and “small government” were bullshit right from the beginning.
Capitalism uses the government no less than any other political ideology to further its interests. The capitalist class needs the state’s monopoly on force to protect private property. That’s why we Marxists call “liberal democracy” the dictatorship of the bourgeoisie, and consider the dictatorship of the proletariat (i.e., a working-class state, for the people) to be true democracy. When there’s any threat to the ruling class (i.e., when the common people have had enough of our oppression, as has been keenly felt in recent years), the rich use fascism to beat back the working class: that’s what we’re seeing now under Trump. The mask has come off: keeping up the illusion of freedom is no longer profitable or sustainable.
The Democratic Party has been every bit as much a part of this rightward movement as has been the GOP. Clinton gutted welfare, helped re-elect Yeltsin, signed the Telecommunications Act of 1996, and bombed Yugoslavia. Obama expanded the Patriot Act, increased surveillance, and punished whistleblowers. Biden didn’t lift a finger to stop Israel’s killing of Palestinians. It’s easy to see how all of this led to Trump, if you have eyes to see.

IX: Conclusion
Liberals are living in a fool’s paradise if they think voting in a Democrat in 2028 will fix the Trump problem. We’ve seen the DNC/GOP one-two punch too many times over the years to believe that any meaningful reversal of the current fascism will happen. The Republicans in power push things disturbingly rightward, the Democrats hypocritically wring their hands about it, and when they are in power, they leave matters largely the same.
On the issue of releasing the unredacted Epstein Files in their entirety, Pam Bondi said the whole system would collapse if they were thus released (Snopes denies she ever said it, but I think one ought to pull a Snopes on Snopes, since so many of us suspect Snopes works for the powers-that-be). Anyway, if true, then in Bondi’s response we can see a hint in why the Democrats won’t reverse the move to the right, but only pay lip service to doing so. Democrats are part of that system, not a cure to it. So many people would go down with Trump et al, not just the Clintons, that the whole legal system would be overwhelmed. I would not be at all surprised if many other high-ranking Democrats would be exposed in the Epstein files, too.
But if that’s the case, so be it, I say. Tear the whole system apart. Burn it to the ground, and replace it with federations of socialist communities that will take care of the needs of the people and restore the land to the aboriginals. The damnation of the empire will be the salvation of the poor and disenfranchised. I won’t state explicitly how the tearing-apart of the system should be done, but I’ll just say this: I’m having visions of tricoteuses.
You must be logged in to post a comment.